SQL injection in RISI - Gestão de Horários (CVE-2019-6491)
RISI Expert Software Solutions more specifically the Gestão de Horário (Schedule Management in English) suffers from a SQL injection in the login form.
Since this is mainly a Human Resources management software by abusing this vulnerability, it is possible to enumerate the database and retrieve sensitive information. Since this application also supports LDAP connectivity to a domain, it is possible to obtain information about that connection and possibly escalate privileges on the domain if the authentication is badly configured.
This vulnerability has been identified by MITRE as CVE-2019-6491.
Scope of the problem
According to RISIs own website, this software is used in several Portugal Hospitals.
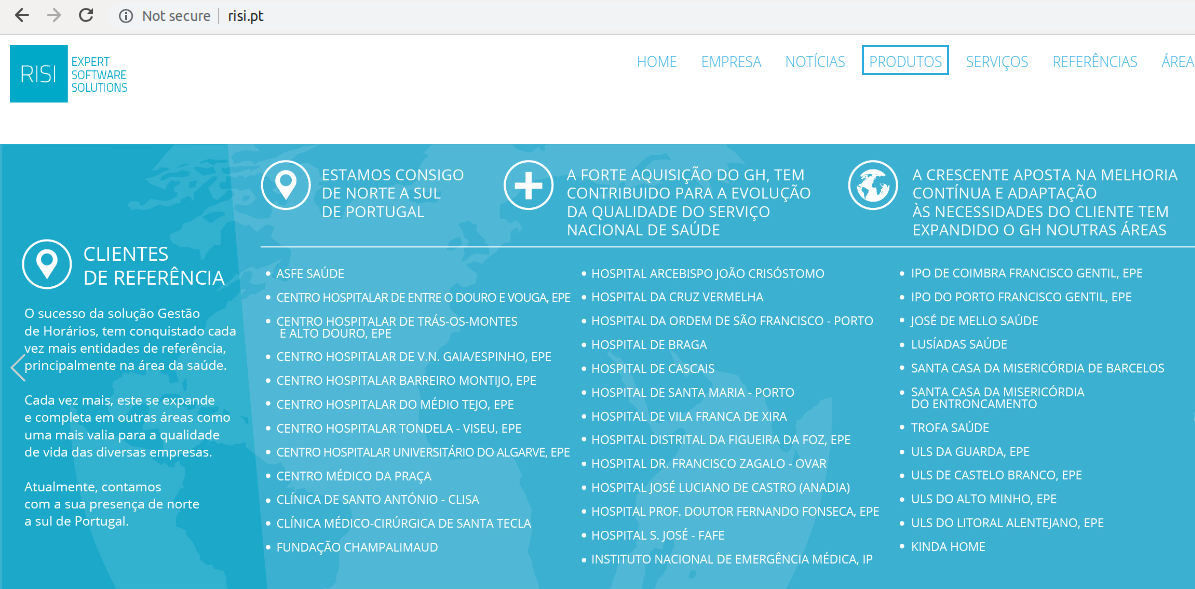
In a quick Google search, we can see that the own National Institute for Medical Emergency (INEM - Instituto Nacional de Emergência Médica) is also supported by this software and belongs to a Network Domain.
This could have severe consequences for those who rely on the safety of their fleet as well as the people who work for INEM.
Problem
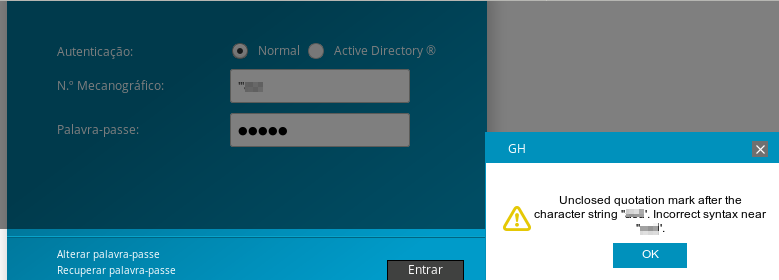
Analyzing the interface we see that there are two ways to login, using Domain credentials or using a “Normal” authentication that uses the underlining database to authenticate the user.

This normal authentication requires an identification number. If we try to write any other character than a Number, the application will block it.
Analyzing the code we can see that a JavaScript Event CheckNumeric is attached to the keyboard and if the check fails, the character is not appended to the string.
However, we can remove or replace this event or even edit the request to insert whatever necessary to exploit the system.
By appending the ‘“qwerty payload, we see an error message regarding the SQL query. This is a good indicator of a SQL injection. Due to the severity of the incident, the correspondent CSIRT was contacted to handle the incident.
A third-party, that wishes to remain anonymous, confirmed that there was indeed an SQL injection vulnerability capable of being leveraged. This would allow an attacker to access the database and all its data.
The txtUser parameter was found to be Union select (NULL) 4 columns and inline query injectable.
The “Normal” authentication should be enable to exploit this vector!
The vulnerability was detected in RISI - Gestão de Horário version 3201.09.08 rev.23. Although fixed, the vendor did not update the version number so a manual confirmation should be made to check for the vulnerability.
The validation of the User ID is now being made in the event and on the server side through an int cast of the value.
Concluding
This vulnerability was considered critical and dealt accordingly with the help of the National CSIRT of Portugal.
The vendor was quick to patch the exposed, vulnerable systems and update the internal services accordingly.
From an outside standpoint, although the risk being there, it seems that no IOC was detected.
This vulnerability was discovered with the help of Professor João Neves. (Thank you)
Timeline
- 18/01/2019 - First contact to request security contact and incident handling
- 19/01/2019 - CVE ID allocated
- 28/01/2019 - Vendor confirmed Fix
- 01/02/2019 - Disclose
References
OWASP-SQL injection Mitigation
I do not promote the exploitation of this vulnerability for malicious purposes. My research was only an academic one without interference or harm to any people.